When trying to conceive, couples may wonder whether to seek fertility treatment and what kind of fertility treatment will best work for them.
Two methods are frequently used to help couples who are having problems getting pregnant:
- The intrauterine insemination (IUI) procedure entails using a speculum to transfer sperm into the uterus.
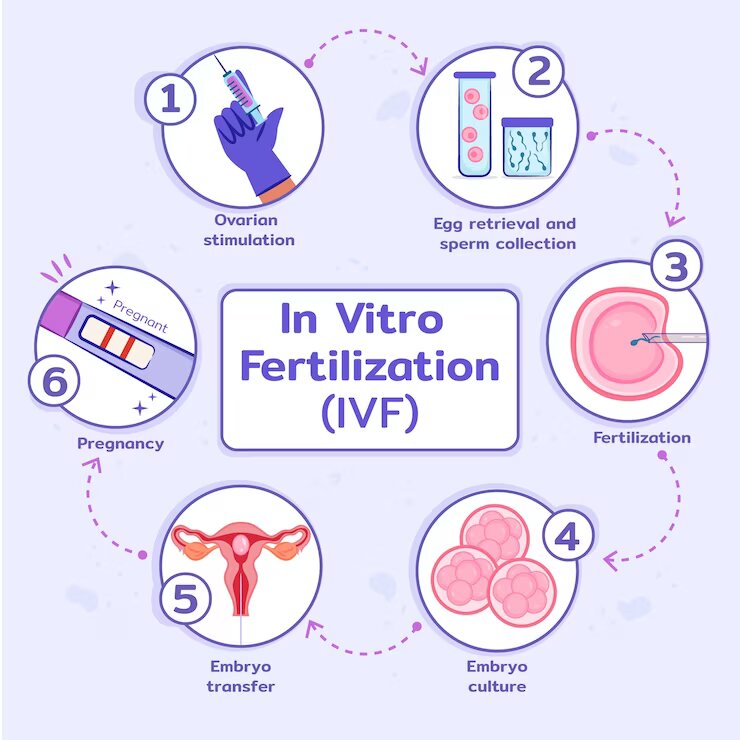
- In-vitro fertilization, often known as IVF, is a surgical procedure that removes eggs from the vagina with the help of a needle that enters through the vagina’s backside. The eggs are subsequently fertilized in a lab environment.
The fertility expert will do various tests, and based on the results of those tests, they will then provide you with information and suggestions regarding alternative treatment options. The specialist will let you know the chances of successfully conceiving a child naturally or after treatment.
Comparing both options will let you know the best approach for you and your partner. This article will give you more quality and let you know about the key differences between IUI and IVF procedures.
Understanding the Key Difference Between IUI and IVF
IUIs Could be More Natural and Less Invasive than Other Procedures
IUI is frequently the initial course of treatment advised for infertile couples because it is far less invasive as compared to IVF. An IUI entails injecting a washed male partner’s sperm into the female patient’s uterus during her fertile window. The process can be performed either naturally as part of the cycle or usually, in conjunction with medical therapy (like letrozole or clomiphene citrate).
The washed sperm has a higher percentage of motile sperm, having a better chance of fertilizing an egg. Sperms do not have to “swim” far for reaching the place where they need to be to fertilize an egg, as they are injected straight into the uterus.
Couples experiencing trouble conceiving due to other factors, such as work, travel schedules, or sexual dysfunction, may benefit from IUI. IUI can help couples facing trouble becoming pregnant for many other reasons besides helping couples who are experiencing infertility problems.
Most women undergoing IUI receive hormones or medications to trigger ovulation or increase the number of eggs that are ovulated every month. To increase their chances of getting pregnant, this procedure is performed.
IVF
For couples having trouble getting pregnant for unexplainable reasons, in vitro fertilization (IUI) can be a good procedure.
IVF treatment is Often Advised for Couples with Any of the Following Difficulties
- Severe infertility in men
- Blockages in the fallopian tubes
- IUI failure to result in pregnancy
- Hereditary disease
Before in vitro fertilization, preimplantation genetic infertility testing, an advanced scientific technique, can be used (IVF). Patients worried about a genetic issue and those who have had many unsuccessful cycles of in vitro fertilization (IVF) or miscarriages may benefit from this treatment. The process can be used to find chromosomal abnormalities or genetic diseases in embryos. It helps in choosing which embryo would be the greatest candidate for transfer.
What Technique Should Be Employed Instead?
It would help if you spoke with a fertility professional to assess your medical history and discuss the next actions that should be followed because each patient and situation is different. It is common for a couple to struggle with infertility, but regardless of their age, it is advised that they get help right away rather than waiting.
What are the Main Differences Between Intrauterine Insemination and In Vitro Fertilization?
The key difference between IVF and IUI is during IUI; fertilization takes place internally. In other words, the woman’s uterus is directly injected with sperm. This implies that the embryo will also implant there if fertilization is successful.
IVF, also referred to as external fertilization, is an assisted reproductive method in which fertilization occurs outside the uterus. The sperm and egg are combined during the fertilization process, and after this stage is finished, the fertilized egg or eggs are chosen, and one or more of them are put into the woman’s uterus. The ideal scenario would be for the egg to attach to the endometrial lining of the uterus after fertilization, resulting in pregnancy and the delivery of a full-term baby or babies.
IUI v/s IVF Success Rate
Compared to IUI, IVF has a much higher success rate. Artificial insemination is less costly and more intrusive than in vitro fertilization (IVF). Three cycles of intrauterine insemination are typically advised for couples before they proceed with in vitro fertilization.
What Distinguishes IUI and IVF from One Another?
Most of the similarities between intrauterine insemination (IUI) and in vitro fertilization (IVF) relate to the initial stages of the therapy and the basic processes of human conception.
Before intrauterine insemination or in vitro fertilization (IVF), or intrauterine insemination (IUI), fertility medications may be used. These medications are used to increase fertilization success rates or promote ovulation and facilitate egg retrieval in the case of IVF. Additionally, these treatments might entail techniques to isolate sperm of the highest caliber from the samples provided for fertilization.
To be successful, an egg must be fertilized for intrauterine insemination (IUI) and in vitro fertilization (IVF). After that, the fertilized egg must deposit itself in the uterine lining and develop into full-term or multiple infants. That sums up the fundamental principles of how a human being is conceived.
The Cost Difference between IUI and IVF
IUI is a type of fertility treatment with a moderately priced price tag. IVF treatment costs about 15,000 Indian Rupees (INR), which covers the price of all required examinations and medications. The expenses connected with the sperm donor’s participation are not included, though.
A simple fertility procedure called IUI therapy shortens the time it takes for sperm to reach the uterus, which reduces the obstacles that must be overcome and increase the chances of a successful pregnancy.
The cost of an in vitro fertilization (IVF) cycle can range from 2.5 to 4 times the lowest yearly salary. You may require additional drugs, tests, and treatments like a frozen embryo transfer, which could raise the price even further.
Compared to In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), is Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) a Better Option?
IUI, is the most common type of fertility treatment, as was previously stated. Fertilization occurs naturally inside the body rather than in any lab and the complete procedure is less invasive. In addition, it’s frequently the first course of treatment for many individuals. Because of this, after the male partner’s ejaculation has been processed, artificial insemination requires the presence of fertile eggs, functional ovaries, and fallopian tubes in addition to the availability of at least 5 motile sperm.
If neither you nor your partner can meet the IUI requirements, you might wish to consider IVF as a backup plan. Numerous infertility issues, including those involving the uterus, fallopian tubes, endometriosis, low sperm count, age-related problems, unexplained infertility, motility, etc, can be treated with IVF. In vitro fertilization may also be successful for those who want to use donated eggs or a surrogate (IVF).
Which is More Painful, IUI or IVF?
The majority of women do not experience any pain during IUI. No anesthesia or medications are necessary, and the procedure can be finished in the clinic in five to ten minutes. It is not uncommon for people to experience moderate bleeding or cramping during or after treatment.
On the other hand, the IVF process is also not painful. Patients can take an oral sedative before the transfer to relax the cervix. Patients could experience some abdominal cramps for the first day or two.
What are the Chances of Getting Pregnant with IUI vs IVF?
Even with just one cycle, IUI offers women under the age of 35 a probability of pregnancy between 10 and 15 percent. In vitro fertilization (IVF) cycles utilizing a woman’s eggs often have a success rate for patients under the age of 35 of between 45 and 50 percent, if not even higher.
When embryos are genetically screened and chosen before the transfer, these success rates can be raised too far higher, frequently in the 60 to 70 percent range.
The success rate of IUI and IVF is significantly higher in younger patients. The success rate for either procedure drops significantly for women over 40 who use their eggs.
Who is a Good Candidate for IUI?
If both of a woman’s fallopian tubes are obstructed, she cannot undergo IUI; at least one must be open. She also needs to have access to a supply of wholesome eggs regularly. She might also be dealing with one or more of the following issues: problems with the cervical mucus that can prevent sperm from reaching the egg.
What is the Age Limit for IUI and IVF?
The recent amendment in ART Bill, which goes into effect in 2020, specifies that a woman must be 50 years old or older to conceive through IVF or assisted conception in India, while a man must be 55 years or older.
The process of IUI therapy must take the patient’s age into account. The number of eggs in a woman’s ovarian reserve and her levels of AMH eventually decline as she ages. As a result, as a woman ages, her chances of getting pregnant decline noticeably. The majority of the time, three rounds of IUI are necessary. However, you can get pregnant after the first cycle if you are under 30, have healthy reproductive organs, and generate high-quality eggs and sperm.
Should I Skip IUI and Go Straight to IVF?
There were some situations where a patient would benefit more from skipping the IUI treatment option and going straight to the IVF stage of their fertility treatment. Each patient will be responsible for making their own decision regarding this topic after thoroughly discussing it with their reproductive specialist.